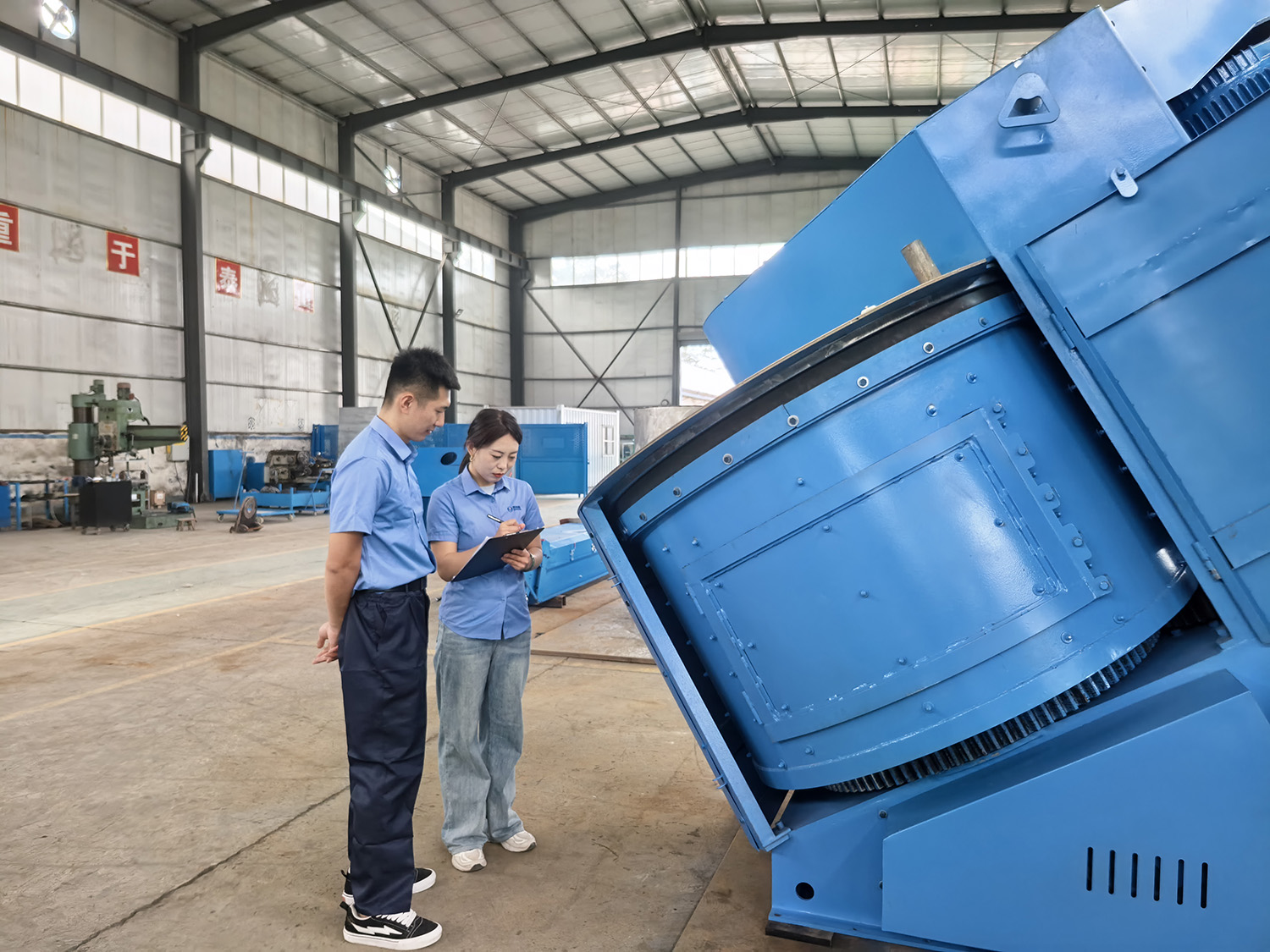
In the design of inclined mixing granulators, the inclination angle is not arbitrarily set but is the result of precise calculations integrating fluid mechanics and materials science. This seemingly simple angle design has become the core key to the efficient operation of the equipment, profoundly influencing mixing uniformity, granulation efficiency, and material adaptability.
Synergy Between Angle and Gravity Enhances Mixing Efficiency
Traditional horizontal granulators rely on the mechanical force of stirring blades to push materials, which easily leads to local accumulation. Inclined equipment, through a golden inclination angle of 15°-30°, enables materials to form a circulating flow field of spiral ascent and free fall under the dual action of gravity and stirring force. This movement trajectory makes materials complete a process of "turning - colliding - fusing" every rotation, increasing the mixing efficiency by 40% compared with horizontal equipment. Moreover, it can break the stratification of materials with different densities, allowing powders and liquid additives to achieve micro-level mixing in a short time.
Traditional horizontal granulators rely on the mechanical force of stirring blades to push materials, which easily leads to local accumulation. Inclined equipment, through a golden inclination angle of 15°-30°, enables materials to form a circulating flow field of spiral ascent and free fall under the dual action of gravity and stirring force. This movement trajectory makes materials complete a process of "turning - colliding - fusing" every rotation, increasing the mixing efficiency by 40% compared with horizontal equipment. Moreover, it can break the stratification of materials with different densities, allowing powders and liquid additives to achieve micro-level mixing in a short time.
Dynamic Angle Adjustment Adapts to Diverse Material Properties
To address the problems that viscous materials are prone to agglomeration and light powders are easy to float, the equipment is designed with a steplessly adjustable inclination angle system. When handling high-viscosity materials (such as ceramic slurries), the angle is increased to 25°-30° to accelerate material flow by gravity and reduce blade wall sticking; when processing powders like light calcium carbonate, the angle is reduced to 15°-20° to extend the residence time of materials in the cylinder, ensuring sufficient mixing. A coating enterprise, by dynamically adjusting the angle, increased the mixing uniformity of pigments and base materials from 82% to 97%, and the product color difference rate decreased by 60%.
To address the problems that viscous materials are prone to agglomeration and light powders are easy to float, the equipment is designed with a steplessly adjustable inclination angle system. When handling high-viscosity materials (such as ceramic slurries), the angle is increased to 25°-30° to accelerate material flow by gravity and reduce blade wall sticking; when processing powders like light calcium carbonate, the angle is reduced to 15°-20° to extend the residence time of materials in the cylinder, ensuring sufficient mixing. A coating enterprise, by dynamically adjusting the angle, increased the mixing uniformity of pigments and base materials from 82% to 97%, and the product color difference rate decreased by 60%.
Linkage Between Angle and Granulation Module Optimizes Forming Quality
The inclination angle forms an ingenious cooperation with the granulation pressure roller: after materials complete pre-mixing in the inclined cylinder, they naturally enter the granulation area along the slope, avoiding particle breakage caused by forced conveying in traditional equipment. At the same time, the pressure gradient generated by the inclination angle makes the materials 受力 more uniformly during granulation, increasing the particle forming rate to over 95% and controlling the particle size deviation within ±0.3mm. This seamless connection design of "mixing - granulation" is particularly suitable for industries such as building materials and fertilizers that have high requirements for particle strength.
The inclination angle forms an ingenious cooperation with the granulation pressure roller: after materials complete pre-mixing in the inclined cylinder, they naturally enter the granulation area along the slope, avoiding particle breakage caused by forced conveying in traditional equipment. At the same time, the pressure gradient generated by the inclination angle makes the materials 受力 more uniformly during granulation, increasing the particle forming rate to over 95% and controlling the particle size deviation within ±0.3mm. This seamless connection design of "mixing - granulation" is particularly suitable for industries such as building materials and fertilizers that have high requirements for particle strength.
The design wisdom of the inclination angle reflects the equipment's precise grasp of the laws of material movement. From mixing efficiency to granulation quality, this detailed design has become the key for inclined mixing granulators to surpass traditional equipment, and also provides more efficient and flexible production solutions for multiple industries.